-
2020.05.11
Background: Maternal pre-postnatal psychosocial distress increases the risk for childhood allergic disease. This may occur through a host immunity pathway that involves intestinal secretory Immuno-globulin A(sIgA). Experimental animal models show changes in the gut microbiome and immunity of offspring when exposed to direct or prenatal maternal stress, but little is known in humans.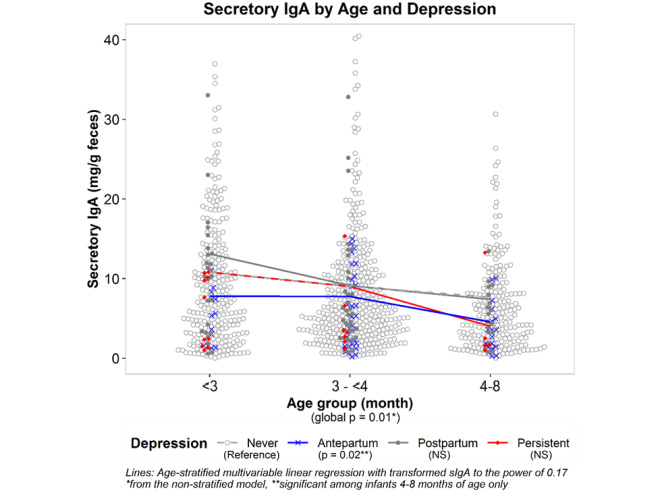 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2020.04.30
Background: An investigator‐driven, real‐life follow‐up study of adult‐onset steroid‐naïve, newly diagnosed asthma (162 patients) to investigate the treatment results over the 25‐year course of the disease and whether the first treatment year's forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) predicts the long‐term prognosis.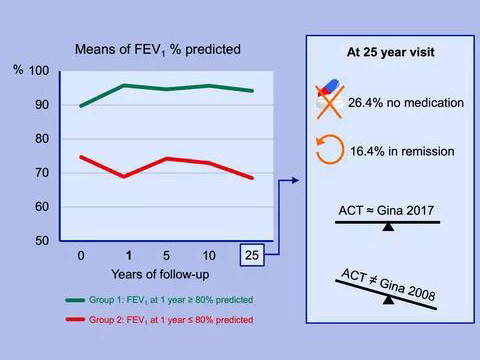 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2020.04.01
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) are least abundant, tightly regulated and IgE producing B cells are rare. The cellular origin and evolution of IgE responses are poorly understood. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2020.04.01
Background: The prevention of food allergy is a key priority for reducing the burden of allergic disease. Environmental exposures modulate the risk of developing food allergy and some of this may be mediated by the infants’ developing microbiome. However, the role of potentially protective environmental exposures, such as pet ownership, is largely uninvestigated with respect to food allergy. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2020.04.01
The clinical presentation of cow's milk protein allergy (CMPA) in children varies. This retrospective study aimed to investigate the prevalence and clinical manifestations of CMPA in young children who visited for evaluation of iron deficiency anemia (IDA). READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.09.23
Background: Biomarkers, preferably noninvasive, that predict asthma inception in children are lacking. Objective: Little is known about biomarkers of type 2 inflammation in early life in relation to asthma inception. We evaluated aeroallergen sensitization, peripheral blood eosinophils, and serum periostin as potential biomarkers of asthma in children. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.09.23
Background: Chronic ocular allergic diseases such as vernal kerato conjunctivitis (VKC) and atopic kerato conjunctivitis (AKC) are accompanied by serious comorbidities; however, the underlying pathogenesis remains obscure. Furthermore, diagnosing conjunctival lesions in patients with atopic dermatitis and estimating the severity in AKC are important for the treatment of ocular allergic diseases. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.08.23
Allergic sensitization, most notably to perennial aeroallergens, has been defined as a pivotal risk factor for the development of asthma. Recently, it has become evident that both the timing of allergic sensitization and the quantity of sensitization are impor-tant prognostic indicators. Simpson et al have identified an atopy phenotype in children they termed multiple early sensitization. In those children sensitized to multiple aeroallergens at an early age, Simpson et al reported a remarkable increase in risk for asthma inception, severe exacerbations leading to hospitalization, and impaired lung function. This link between early-life sensitization to multiple allergens and increased asthma risk has been replicated in additional cohort studies. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.08.09
Atopic dermatitis (AD), food allergy, allergic rhinitis, and asthma are common atopic disorders of complex etiology. The frequently observed atopic march from early AD to asthma, allergic rhinitis, or both later in life and the extensive comorbidity of atopic disorders suggest common causal mechanisms in addition to distinct ones. Indeed, both disease-specific and shared genomic regions exist for atopic disorders. Their prevalence also varies among races; for example, AD and asthma have a higher prevalence in African Americans when compared with European Americans. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.07.31
Background: Macrophages can be converted in vitro into immunoregulatory M2b macrophages in the presence of immune complexes (ICs), but the role of the specific subclasses IgG1 or IgG4 in this phenotypic and functional change is not known.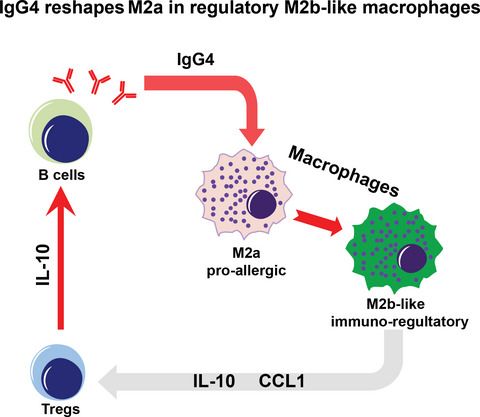 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.06.26
Weather and climate change are constant and ever-changing processes that affect allergy and asthma. The purpose of this report is to provide information since the last climate change review with a focus on asthmatic disease. PubMed and Internet searches for topics included climate and weather change, air pollution, particulates, greenhouse gasses, traffic, insect habitat, and mitigation in addition to references contributed by the individual authors. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.06.26
Methods: This nationwide Swedish cohort study of 1,086,378 children born in Sweden in 2001-2012 used prospectively recorded data from health care registers. Using Cox regression,we estimated hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% CIs for the association between perinatal characteristics (eg, cesarean delivery and preterm birth) and food allergy as defined by diagnoses in the National Patient Register, adjusting for infant sex and maternal factors (age at delivery, country of birth, parity, smoking, body mass index, and asthma/pulmonary disease). READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.06.06
Allergic and nonallergic asthma severity in children can be affected by microbial exposures. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.06.06
Dynamic establishment of the nasal microbiota in early life influences local mucosal immune responses and susceptibility to childhood respiratory disorders. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.06.06
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is often characterized by local production of polyclonal IgE idiotypes. Although tissue IgE concentrations can be in the range of several thousand kilounits per liter, the regulatory mechanisms by which IgE-mediated inflammation is controlled in patients with nasal polyps are not well understood. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.30
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is a TH1 lymphocyte–biased fibrosing alveolitis caused by antigens ranging from avian excreta, fungi, thermophilic bacteria, and protozoa to reactive chemicals found in the workplace. Mimicking a viral syndrome, acute exposures to inciting antigens cause abrupt onset of nonproductive cough, dyspnea, and chills with arthralgias or malaise usually from 4 to 8 hours later so that the temporal relationship between antigen exposure and symptoms might be unsuspected. The histology of HP reveals prominent lymphocyte infiltrates that thicken the alveolar septa with poorly formed granulomas or giant cells.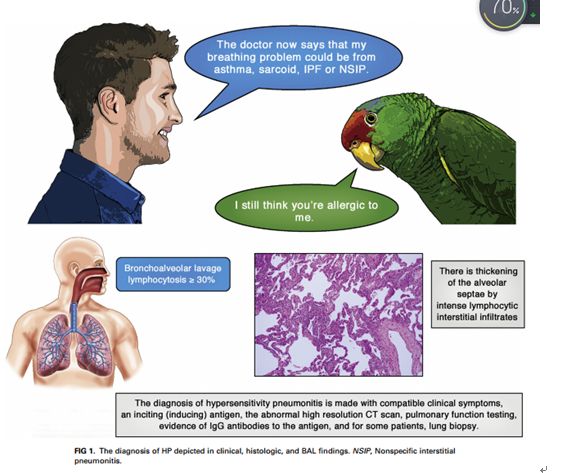 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.30
Allergen-specific IgE measurements and the clinical history are the cornerstones of allergy diagnosis. During the past decades, both characterization and standardization of allergen extracts and assay technology have improved. Here we discuss the uses, advantages, misinterpretations, and limitations of ImmunoCAP IgE assays (Thermo Fisher Scientific/Phadia, Uppsala, Sweden) in the field of allergology. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.15
The extensive use of allergen molecules in birth cohort studies revealed that atopic sensitization is a sequential IgE response to distinct non–cross-reacting molecules from the same allergenic source (ie, molecular spreading), starting with an initiator molecule. This phenomenon reaches different degrees of progression (monomolecular, oligomolecular, and polymolecular) according to the individual atopic propensity and allergen exposure, thus producing an extreme heterogeneity of IgE sensitization profiles in patient populations. In patients with allergic rhinitis, the broader the IgE molecular sensitization profile, the greater is the risk of asthma and other allergic comorbidities, such as oral allergy syndrome. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.15
Primary human blood-derived mast cells (MCs) were generated from peripheral blood precursors, sensitized with patients' sera, and then incubated with allergen. MC degranulation was assessed by means of flow cytometry and mediator release. We compared the diagnostic performance of MATs with that of existing diagnostic tools to assess in a cohort of peanut-sensitized subjects undergoing double-blind, placebo-controlled challenge.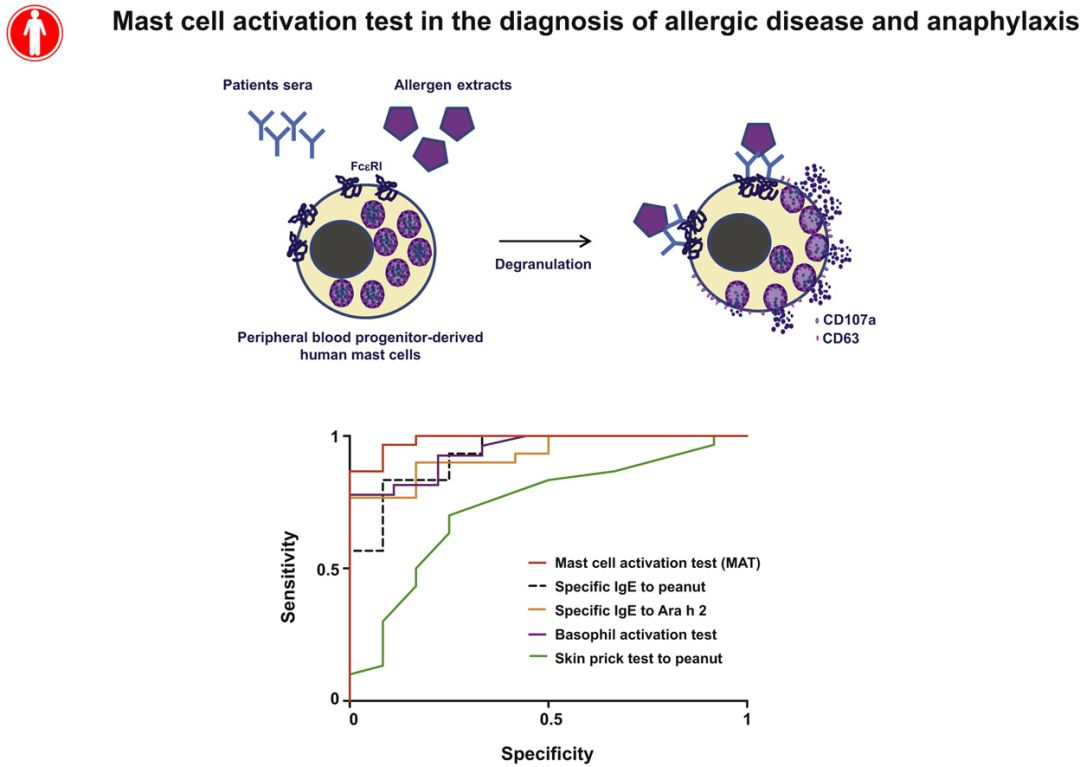 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.04
Understanding differences in allergen immunotherapy products and practices in North AmericaAllergen immunotherapy (AIT) is thought to be clinically effective and safe in treating allergic rhinitis, asthma, and stinging insect allergy in Europe and North America. However, there are intercontinental differences in AIT therapeutic products in terms of their application and regulation. READ MORE
READ MORE
MK手机投注 | 安博·体育(中国)有限公司-官网 | 乐动官方网站 | 星空手机版 | 星空手机版 | mk体育(MKsports集团)股份公司 | 安博手机网页版登录入口 | 华体平台 | 千亿体育官网在线登录入口中国有限公司 |
 华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
