-
2020.07.03
Background: Caesarean delivery (C‐section) may disrupt maternal‐infant microbial transfer and alter immune system development and subsequent risk for atopic dermatitis. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.15
Background: There is an increasing interest in targeted application of probiotic bacteria for prevention and treatment of airway diseases, including allergies. Here, we investigated the beneficial effects of preventive intranasal treatment with probiotics Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and L. rhamnosus GR-1 in a mouse model of allergic asthma.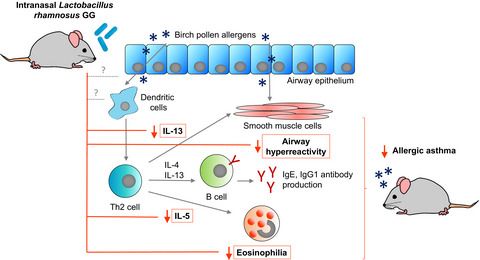 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.15
Asthma is the most prevalent chronic disease of childhood. Recently, we identified a critical window early in the life of both mice and Canadian infants during which gut microbial changes (dysbiosis) affect asthma development. Given geographic differences in human gut microbiota worldwide, we studied the effects of gut microbial dysbiosis on atopic wheeze in a population living in a distinct developing world environment.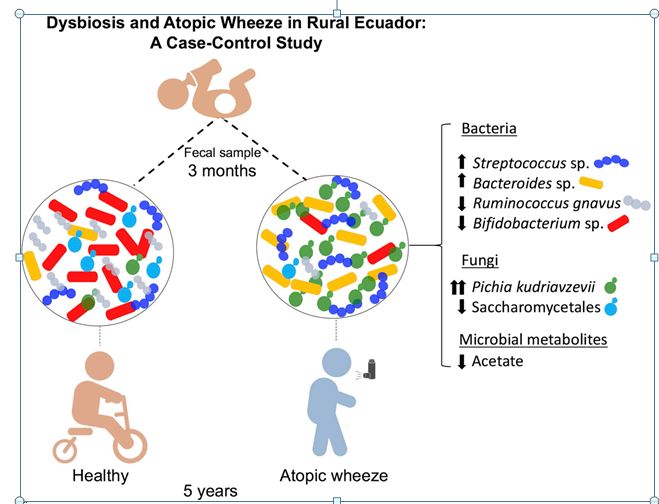 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.15
The intestinal microbiota plays an important role in development of the immune system and regulation of immune responses. This review summarizes the association between the intestinal microbiota and the development of allergic sensitization, eczema, and asthma in neonates and children. Overall, a greater relative abundance of Bacteroidaceae, Clostridiaceae, and Enterobacteriaceae and a lower relative abundance of Bifidobacteriaceae and Lactobacillaceae is associated with the development of allergic sensitization, eczema, or asthma. Reduced bacterial diversity can be associated with the development of allergic disease. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.04
Oral microbiota maturation during the first 7 years of life in relation to allergy developmentBackground: Allergic diseases have become a major public health problem in affluent societies. Microbial colonization early in life seems to be critical for instructing regulation on immune system maturation and allergy development in children. Even though the oral cavity is the first site of encounter between a majority of foreign antigens and the immune system, the influence of oral bacteria on allergy development has not yet been reported.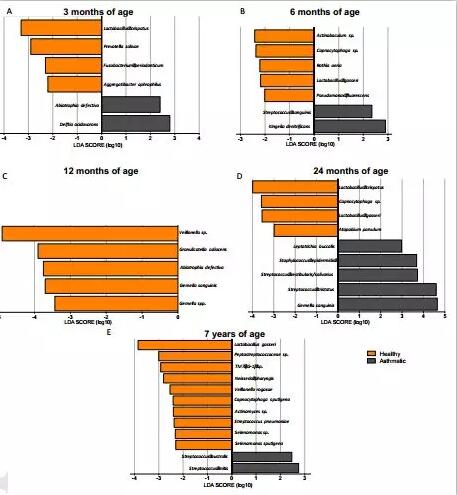 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.04.04
Integrative Analysis of the Intestinal Metabolome of Childhood AsthmaBackground The intestinal metabolome reflects biological consequences of diverse exposures and may provide insight into asthma pathophysiology.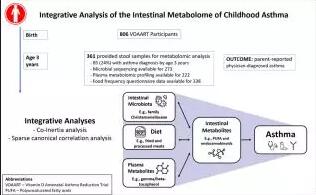 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.03.01
As an interface with the environment, the skin is a complex ecosystem colonized by many microorganisms that coexist in an established balance. The cutaneous microbiome inhibits colonization with pathogens, such as Staphylococcus aureus, and is a crucial component for function of the epidermal barrier. Moreover, crosstalk between commensals and the immune system is now recognized because microorganisms can modulate both innate and adaptive immune responses. Host-commensal interactions also have an effect on the developing immune system in infants and, subsequently, the occurrence of diseases, such as asthma and atopic dermatitis (AD).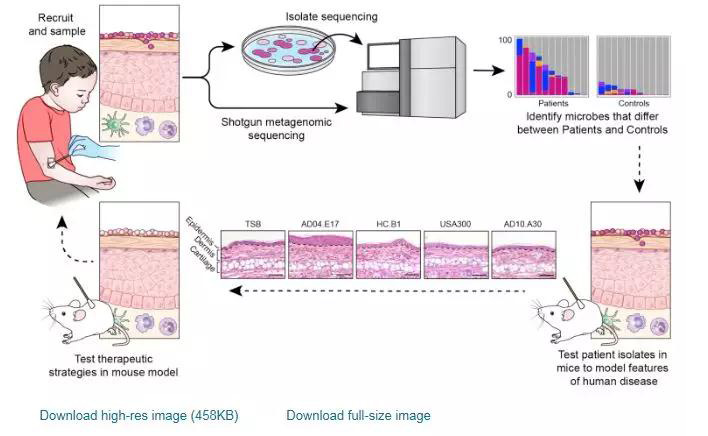 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2019.01.02
Food allergy is a serious disease worldwide; it can significantly lower the standard of living of affected individuals and may be life-threatening. In particular, hypersensitivity to seafood has been increasing in recent years owing to rising consumption. The mucosal immune system plays a critical role in the onset of seafood allergy and other allergic diseases. Recently, experimental and clinical evidence has shown that probiotics significantly modulate immune responses and thus suppress allergic reactions.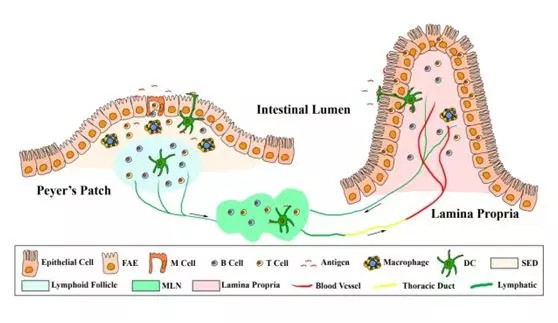 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2018.11.13
Food allergy is a common disease affecting approximately 8% of children and 5% of adults. The prevalence has increased over the last two decades, suggesting an important environmental contribution to susceptibility. Studies have identified mode of birth, pet exposure, and having older siblings as being significant risk modifying factors in the development of food allergy. With the discovery that these factors significantly impact the composition of the intestinal microbiome, which is known to play a critical role in shaping the immune system, recent studies have begun to address the role of the intestinal microbiota in the development of food allergy. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2018.11.13
The application of recently developed sensitive, specific, culture-independent tools for identification of microbes is transforming concepts of microbial ecology, including concepts of the relationships between the vast complex populations of microbes associated with ourselves and with states of health and disease. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2018.11.13
PRACTALL is a joint initiative of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology and the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology to provide shared evidence-based recommendations on cutting-edge topics in the field of allergy and immunology. PRACTALL 2017 is focused on what has been established regarding the role of the microbiome in patients with asthma, atopic dermatitis, and food allergy. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2018.11.13
Ingestion of innocuous antigens, including food proteins, normally results in local and systemic immune nonresponsiveness in a process termed oral tolerance. Oral tolerance to food proteins is likely to be intimately linked to mechanisms that are responsible for gastrointestinal tolerance to large numbers of commensal microbes. Here we review our current understanding of the immune mechanisms responsible for oral tolerance and how perturbations in these mechanisms might promote the loss of oral tolerance and development of food allergies.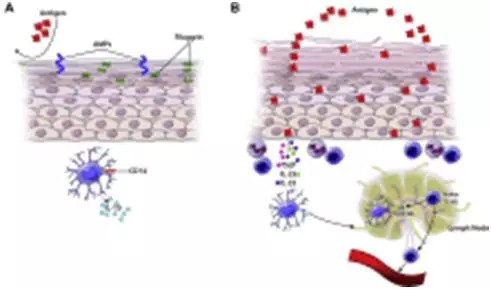 READ MORE
READ MORE -
2018.11.13
We studied 226 children with milk allergy who were enrolled at infancy in the Consortium of Food Allergy observational study of food allergy. Fecal samples were collected at age 3 to 16 months, and the children were followed longitudinally with clinical evaluation, milk-specific IgE levels, and milk skin prick test performed at enrollment, 6 months, 12 months, and yearly thereafter up until age 8 years. READ MORE
READ MORE -
2018.11.13
Probiotics are live microorganisms that confer a health benefit on the host when applied in adequate amounts. The therapeutic effects of probiotics have been mostly studied in the gastrointestinal tract, but recent evidence points towards the potential of these bacteria to prevent and/or treat chronic airway diseases.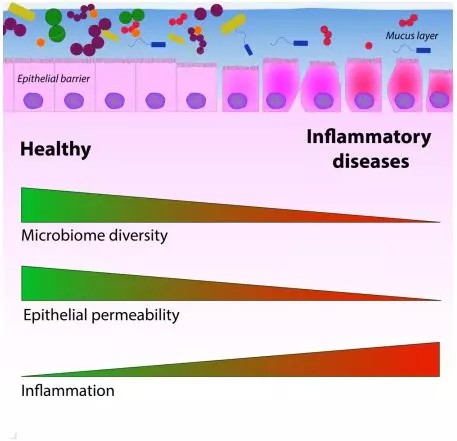 READ MORE
READ MORE
MK手机投注 | 安博·体育(中国)有限公司-官网 | 乐动官方网站 | 星空手机版 | 星空手机版 | mk体育(MKsports集团)股份公司 | 安博手机网页版登录入口 | 华体平台 | 千亿体育官网在线登录入口中国有限公司 |
 华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
