Release date:2023-10-31
Clin Exp Allergy
[IF: 5.131]
Fungi and bacteria in the beds of rural and urban infants correlate with later risk of atopic diseases
DOI: 10.1111/cea.14414
Abstract:
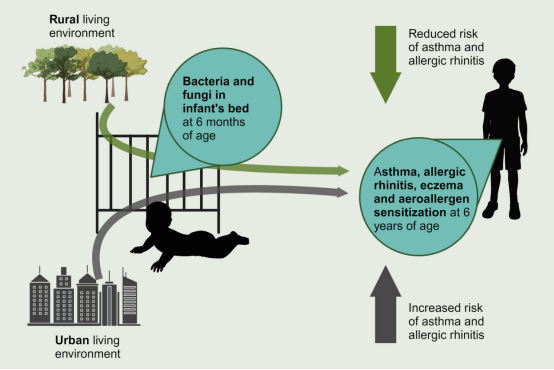
Introduction:Rural children have a lower risk of asthma and atopic diseases than urban children. However, whether indoor microbiota in non-farming rural homes provides protection is unclear.
Methods:Here, we examine if microbes in the beds of rural and urban infants are associated with later development of atopic diseases. We studied fungi and bacteria in the beds of 6-month-old infants (n = 514) in association with the risk of asthma, allergic rhinitis, eczema and aeroallergen sensitization at 6 years of age in the prospective COPSAC2010 cohort.
Results:Both fungal and bacterial diversity were lower in the beds of children, who later developed allergic rhinitis (−0.22 [−0.43,−0.01], padj = .04 and −.24 [−0.42,−0.05], padj = .01 respectively) and lower bacterial richness was discovered in beds of children later developing asthma (−41.34 [−76.95,−5.73], padj = .02) or allergic rhinitis (−45.65[−81.19,−10.10], padj = .01). Interestingly, higher fungal diversity and richness were discovered in the beds of children developing eczema (0.23 [0.02,0.43], padj = .03 and 29.21 [1.59,56.83], padj = .04 respectively). We defined a limited set of fungal and bacterial genera that predicted rural/urban environment. Some rural-associated bacterial genera such as Romboutsia and Bacillus and fungal genera Spegazzinia and Physcia were also associated with reduced risk of diseases, including eczema. These fungal and bacterial fingerprints predicting the living environment were associated with asthma and allergic rhinitis, but not eczema, with rural compositions being protective. The bed dust bacteria mediated 27% of the protective association of a rural living environment for allergic rhinitis (p = .04).
Conclusions:Bed dust microbes can be differentially associated with airway- and skin-related diseases. The differing bed dust microbiota between rural and urban infants may influence their later risk of asthma and allergic rhinitis.
First Author:
Jenni Lehtimäki
Corresponding author:
Jakob Stokholm
Correspondence:
COPSAC, Copenhagen Prospective Studies on Asthma in Childhood, Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Ledreborg Alle 34, Gentofte 2820, Denmark.
Email: stokholm@copsac.com
[IF: 5.131]
Fungi and bacteria in the beds of rural and urban infants correlate with later risk of atopic diseases
DOI: 10.1111/cea.14414
Abstract:
Introduction:Rural children have a lower risk of asthma and atopic diseases than urban children. However, whether indoor microbiota in non-farming rural homes provides protection is unclear.
Methods:Here, we examine if microbes in the beds of rural and urban infants are associated with later development of atopic diseases. We studied fungi and bacteria in the beds of 6-month-old infants (n = 514) in association with the risk of asthma, allergic rhinitis, eczema and aeroallergen sensitization at 6 years of age in the prospective COPSAC2010 cohort.
Results:Both fungal and bacterial diversity were lower in the beds of children, who later developed allergic rhinitis (−0.22 [−0.43,−0.01], padj = .04 and −.24 [−0.42,−0.05], padj = .01 respectively) and lower bacterial richness was discovered in beds of children later developing asthma (−41.34 [−76.95,−5.73], padj = .02) or allergic rhinitis (−45.65[−81.19,−10.10], padj = .01). Interestingly, higher fungal diversity and richness were discovered in the beds of children developing eczema (0.23 [0.02,0.43], padj = .03 and 29.21 [1.59,56.83], padj = .04 respectively). We defined a limited set of fungal and bacterial genera that predicted rural/urban environment. Some rural-associated bacterial genera such as Romboutsia and Bacillus and fungal genera Spegazzinia and Physcia were also associated with reduced risk of diseases, including eczema. These fungal and bacterial fingerprints predicting the living environment were associated with asthma and allergic rhinitis, but not eczema, with rural compositions being protective. The bed dust bacteria mediated 27% of the protective association of a rural living environment for allergic rhinitis (p = .04).
Conclusions:Bed dust microbes can be differentially associated with airway- and skin-related diseases. The differing bed dust microbiota between rural and urban infants may influence their later risk of asthma and allergic rhinitis.
First Author:
Jenni Lehtimäki
Corresponding author:
Jakob Stokholm
Correspondence:
COPSAC, Copenhagen Prospective Studies on Asthma in Childhood, Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Ledreborg Alle 34, Gentofte 2820, Denmark.
Email: stokholm@copsac.com
MK手机投注 | 安博·体育(中国)有限公司-官网 | 乐动官方网站 | 星空手机版 | 星空手机版 | mk体育(MKsports集团)股份公司 | 安博手机网页版登录入口 | 华体平台 | 千亿体育官网在线登录入口中国有限公司 |
 华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
