Allergy:全球儿童和成人慢性荨麻疹的患病率
发布日期:2020-05-27
原标题:全球儿童和成人慢性荨麻疹的患病率:荟萃分析系统评价
方法:我们在PUBMED和EMBASE中进行了系统搜索,包括基于人群的横断面或队列设计研究,以及基于健康保险/系统数据库的研究,使用特定的研究工具评估偏倚的风险。对于荟萃分析,我们使用了随机效应模型。
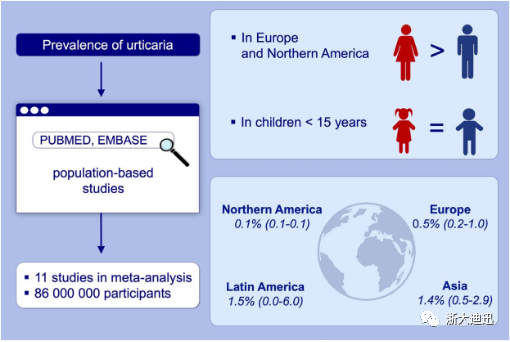
结果:本研究包括18项系统评价和11项荟萃分析,包括来自超过8600万参与者的数据。偏倚风险是中等的,但研究之间的统计异质性(I2)高。亚洲研究综合显示,慢性荨麻疹的患病率较高(1.4%,95%-CI 0.5-2.9),高于欧洲(0.5%,0.2-1.0)和北美(0.1%,0.1-0.1)。女性患病的程度略高于男性,而在15岁以下的儿童中,患病率没有性别差异。检验时间趋势的四项研究表明,随着时间的推移,慢性荨麻疹的患病率呈上升趋势。
结论:在全球范围内,慢性荨麻疹的患病率显示出很大的地区差异。有必要获取更多基于性别的,基于人口的标准化国际数据,尤其是针对儿童和青少年,不同的慢性荨麻疹亚型以及潜在的风险和保护因素。
延伸阅读
Allergy
DOI: 10.1111/all.14037
Abstract:
Background: Urticaria is a frequent skin condition, but reliable prevalence estimates from population studies particularly of the chronic form are scarce.The objective of this study was to systematically evaluate and summarize the prevalence of chronic urticaria by evaluating population‐based studies worldwide. Methods: We performed a systematic search in PUBMED and EMBASE for population‐based studies of cross‐sectional or cohort design and studies based on health insurance/system databases. Risk of bias was assessed using a specific tool for prevalence studies. For meta‐analysis, we used a random effects model.
Results: Eighteen studies were included in the systematic evaluation and 11 in the meta‐analysis including data from over 86 000 000 participants. Risk of bias was mainly moderate, whereas the statistical heterogeneity (I2) between the studies was high. Asian studies combined showed a higher point prevalence of chronic urticaria (1.4%, 95%‐CI 0.5‐2.9) than those from Europe (0.5%, 0.2‐1.0) and Northern American (0.1%, 0.1‐0.1). Women were slightly more affected than men, whereas in children < 15 years we did not find a sex‐specific difference in the prevalence. The four studies that examined time trends indicated an increasing prevalence of chronic urticaria over time.
Conclusion: On a global level, the prevalence of chronic urticaria showed considerable regional differences. There is a need to obtain more sex‐specific population based and standardized international data particularly for children and adolescents,different chronic urticaria subtypes and potential risk and protective factors.
First Author:
Julia Fricke
Correspondence:
Julia Fricke, Institute for Social Medicine,Epidemiology and Health Economics,Charité‐Universitätsmedizin Berlin,Luisenstr. 57, 10117 Berlin, Germany.
All Authors:
Julia Fricke, Gabriela Ávila, Theresa Keller, Karsten Weller, Susanne Lau, Marcus Maurer, Torsten Zuberbier, homas Keil

——浙大迪迅 译
背景:荨麻疹是一种常见的皮肤病,但从人群研究尤其是慢性荨麻疹的研究中获得可靠的评估是很少见的。本研究的目的是通过对世界范围内基于人群研究进行系统地评估,总结慢性荨麻疹的患病率。方法:我们在PUBMED和EMBASE中进行了系统搜索,包括基于人群的横断面或队列设计研究,以及基于健康保险/系统数据库的研究,使用特定的研究工具评估偏倚的风险。对于荟萃分析,我们使用了随机效应模型。
结果:本研究包括18项系统评价和11项荟萃分析,包括来自超过8600万参与者的数据。偏倚风险是中等的,但研究之间的统计异质性(I2)高。亚洲研究综合显示,慢性荨麻疹的患病率较高(1.4%,95%-CI 0.5-2.9),高于欧洲(0.5%,0.2-1.0)和北美(0.1%,0.1-0.1)。女性患病的程度略高于男性,而在15岁以下的儿童中,患病率没有性别差异。检验时间趋势的四项研究表明,随着时间的推移,慢性荨麻疹的患病率呈上升趋势。
结论:在全球范围内,慢性荨麻疹的患病率显示出很大的地区差异。有必要获取更多基于性别的,基于人口的标准化国际数据,尤其是针对儿童和青少年,不同的慢性荨麻疹亚型以及潜在的风险和保护因素。

延伸阅读
Allergy
[IF:6.048]
Prevalence of chronic urticaria in children and adults across the globe: Systematic review with meta‐analysis DOI: 10.1111/all.14037
Abstract:
Background: Urticaria is a frequent skin condition, but reliable prevalence estimates from population studies particularly of the chronic form are scarce.The objective of this study was to systematically evaluate and summarize the prevalence of chronic urticaria by evaluating population‐based studies worldwide. Methods: We performed a systematic search in PUBMED and EMBASE for population‐based studies of cross‐sectional or cohort design and studies based on health insurance/system databases. Risk of bias was assessed using a specific tool for prevalence studies. For meta‐analysis, we used a random effects model.
Results: Eighteen studies were included in the systematic evaluation and 11 in the meta‐analysis including data from over 86 000 000 participants. Risk of bias was mainly moderate, whereas the statistical heterogeneity (I2) between the studies was high. Asian studies combined showed a higher point prevalence of chronic urticaria (1.4%, 95%‐CI 0.5‐2.9) than those from Europe (0.5%, 0.2‐1.0) and Northern American (0.1%, 0.1‐0.1). Women were slightly more affected than men, whereas in children < 15 years we did not find a sex‐specific difference in the prevalence. The four studies that examined time trends indicated an increasing prevalence of chronic urticaria over time.
Conclusion: On a global level, the prevalence of chronic urticaria showed considerable regional differences. There is a need to obtain more sex‐specific population based and standardized international data particularly for children and adolescents,different chronic urticaria subtypes and potential risk and protective factors.
First Author:
Julia Fricke
Correspondence:
Julia Fricke, Institute for Social Medicine,Epidemiology and Health Economics,Charité‐Universitätsmedizin Berlin,Luisenstr. 57, 10117 Berlin, Germany.
All Authors:
Julia Fricke, Gabriela Ávila, Theresa Keller, Karsten Weller, Susanne Lau, Marcus Maurer, Torsten Zuberbier, homas Keil
2020-02-17 Article
创建过敏性疾病的科研、科普知识交流平台,为过敏患者提供专业诊断、治疗、预防的共享平台。
MK手机投注 | 安博·体育(中国)有限公司-官网 | 乐动官方网站 | 星空手机版 | 星空手机版 | mk体育(MKsports集团)股份公司 | 安博手机网页版登录入口 | 华体平台 | 千亿体育官网在线登录入口中国有限公司 |
 华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
华亿体育(中国)游戏平台

