Allergy:重症哮喘中的外周气道2型炎症、中性粒细胞增多症和微生物失调
发布日期:2021-08-06
原标题:严重哮喘患者的外周气道2型炎症、中性粒细胞增多症和微生物失调
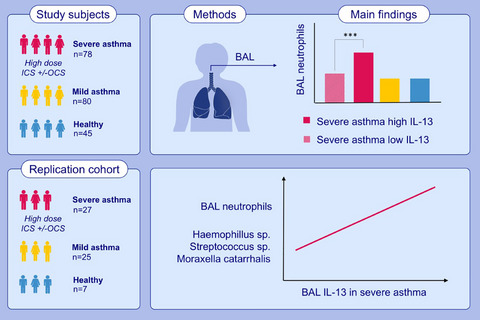
方法:支气管肺泡灌洗液(BAL)样本来自203名哮喘患者和健康志愿者,其中78名为重症哮喘。使用多细胞因子免疫测定平台测量炎症介质。使用末端限制性片段长度多态性方法对另外59名志愿者的BAL样品重复进行16S rRNA分析。
结果:尽管接受了大剂量吸入性糖皮质激素治疗,重症哮喘患者BAL中 IL-13增高,具有高浓度BAL IL-13的重症哮喘患者与具有正常BAL IL-13浓度的患者相比,其肺功能更差,中性粒细胞百分比显著增高,但嗜酸性粒细胞比例没有差异。这一发现在第二个队列中得到了重复,这进一步将BAL IL-13和中性粒细胞增多症与外周气道中潜在致病菌联系起来。
结论:我们的研究结果表明,IL-13的类固醇无效与重症哮喘患者的BAL中性粒细胞增多症和细菌失调有关。我们的研究结果强调了重症哮喘的生物学复杂性,以及更好地了解这种疾病外周气道中的先天性和适应性免疫反应的重要性。
延伸阅读
Allergy
DOI: 10.1111/all.14732
Abstract:
Background: IL-13 is an archetypal T2 cytokine central to the clinical disease expression of asthma. The IL-13 response genes, which are upregulated in central airway bronchial epithelial of asthma patients, can be normalized by high-dose inhaled steroid therapy in severe asthma. However, this is not the case within the peripheral airways. We have sought to further understand IL-13 in the peripheral airways in severe asthma through bronchoalveolar analysis.
Methods: Bronchoalveolar lavage samples were collected from 203 asthmatic and healthy volunteers, including 78 with severe asthma. Inflammatory mediators were measured using a multiple cytokine immunoassay platform. This analysis was replicated in a further 59 volunteers, in whom 16S rRNA analysis of BAL samples was undertaken by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism.
Results: Severe asthma patients with high BAL IL-13, despite treatment with high-dose inhaled corticosteroids, had more severe lung function and significantly higher BAL neutrophil percentages, but not BAL eosinophils than those with normal BAL-13 concentrations. This finding was replicated in the second cohort, which further associated BAL IL-13 and neutrophilia with a greater abundance of potentially pathogenic bacteria in the peripheral airways.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate a steroid unresponsive source of IL-13 that is associated with BAL neutrophilia and bacterial dysbiosis in severe asthma. Our findings highlight the biological complexity of severe asthma and the importance of a greater understanding of the innate and adaptive immune responses in the peripheral airways in this disease.
First Author:
Adnan Azim
Correspondence:
Peter Howarth, Clinical & Experimental Sciences Academic Unit, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK.
All Authors:
Adnan Azim, Ben Green, Laurie Lau, Hitasha Rupani, Nivenka Jayasekera, Kenneth Bruce, Peter Howarth
2021-08-02 Article
创建过敏性疾病的科研、科普知识交流平台,为过敏患者提供专业诊断、治疗、预防的共享平台。


——浙大迪迅 译
背景:IL-13被认为是哮喘临床诊断指标中的典型T2型细胞因子。重症哮喘患者可通过吸入高剂量的类固醇来调节中央气道支气管上皮的IL-13应答基因。然而,在外周气道内情况并非如此。我们试图通过分析支气管肺泡来进一步了解重症哮喘患者外周气道中的 IL-13。方法:支气管肺泡灌洗液(BAL)样本来自203名哮喘患者和健康志愿者,其中78名为重症哮喘。使用多细胞因子免疫测定平台测量炎症介质。使用末端限制性片段长度多态性方法对另外59名志愿者的BAL样品重复进行16S rRNA分析。
结果:尽管接受了大剂量吸入性糖皮质激素治疗,重症哮喘患者BAL中 IL-13增高,具有高浓度BAL IL-13的重症哮喘患者与具有正常BAL IL-13浓度的患者相比,其肺功能更差,中性粒细胞百分比显著增高,但嗜酸性粒细胞比例没有差异。这一发现在第二个队列中得到了重复,这进一步将BAL IL-13和中性粒细胞增多症与外周气道中潜在致病菌联系起来。
结论:我们的研究结果表明,IL-13的类固醇无效与重症哮喘患者的BAL中性粒细胞增多症和细菌失调有关。我们的研究结果强调了重症哮喘的生物学复杂性,以及更好地了解这种疾病外周气道中的先天性和适应性免疫反应的重要性。

延伸阅读
Allergy
[IF:13.146]
Peripheral airways type 2 inflammation, neutrophilia and microbial dysbiosis in severe asthmaDOI: 10.1111/all.14732
Abstract:
Background: IL-13 is an archetypal T2 cytokine central to the clinical disease expression of asthma. The IL-13 response genes, which are upregulated in central airway bronchial epithelial of asthma patients, can be normalized by high-dose inhaled steroid therapy in severe asthma. However, this is not the case within the peripheral airways. We have sought to further understand IL-13 in the peripheral airways in severe asthma through bronchoalveolar analysis.
Methods: Bronchoalveolar lavage samples were collected from 203 asthmatic and healthy volunteers, including 78 with severe asthma. Inflammatory mediators were measured using a multiple cytokine immunoassay platform. This analysis was replicated in a further 59 volunteers, in whom 16S rRNA analysis of BAL samples was undertaken by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism.
Results: Severe asthma patients with high BAL IL-13, despite treatment with high-dose inhaled corticosteroids, had more severe lung function and significantly higher BAL neutrophil percentages, but not BAL eosinophils than those with normal BAL-13 concentrations. This finding was replicated in the second cohort, which further associated BAL IL-13 and neutrophilia with a greater abundance of potentially pathogenic bacteria in the peripheral airways.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate a steroid unresponsive source of IL-13 that is associated with BAL neutrophilia and bacterial dysbiosis in severe asthma. Our findings highlight the biological complexity of severe asthma and the importance of a greater understanding of the innate and adaptive immune responses in the peripheral airways in this disease.
First Author:
Adnan Azim
Correspondence:
Peter Howarth, Clinical & Experimental Sciences Academic Unit, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK.
All Authors:
Adnan Azim, Ben Green, Laurie Lau, Hitasha Rupani, Nivenka Jayasekera, Kenneth Bruce, Peter Howarth
2021-08-02 Article
创建过敏性疾病的科研、科普知识交流平台,为过敏患者提供专业诊断、治疗、预防的共享平台。


MK手机投注 | 安博·体育(中国)有限公司-官网 | 乐动官方网站 | 星空手机版 | 星空手机版 | mk体育(MKsports集团)股份公司 | 安博手机网页版登录入口 | 华体平台 | 千亿体育官网在线登录入口中国有限公司 |
 华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
华亿体育(中国)游戏平台

