JACI:室内微生物群落与哮喘的相关性研究
发布日期:2019-06-06
原标题:室内微生物群落:对儿童哮喘严重程度的影响
延伸阅读
JACI
[IF:13.1]
Indoor microbial communities: Influence on asthma severity in atopic and nonatopic children
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.11.027
Abstract:
Background
Allergic and nonallergic asthma severity in children can be affected by microbial exposures.
Objective
We sought to examine associations between exposures to household microbes and childhood asthma severity stratified by atopic status.
Methods
Participants (n = 196) were selected from a cohort of asthmatic children in Connecticut and Massachusetts. Children were grouped according to asthma severity (mild with no or minimal symptoms and medication or moderate to severe persistent) and atopic status (determined by serum IgE levels). Microbial community structure and concentrations in house dust were determined by using next-generation DNA sequencing and quantitative PCR. Logistic regression was used to explore associations between asthma severity and exposure metrics, including richness, taxa identification and quantification, community composition, and concentration of total fungi and bacteria.
Results
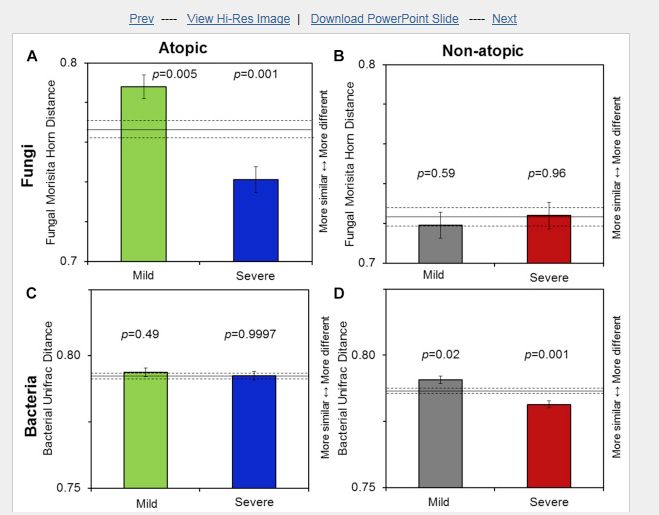
Among all children, increased asthma severity was significantly associated with an increased concentration of summed allergenic fungal species, high total fungal concentrations, and high bacterial richness by using logistic regression in addition to microbial community composition by using the distance comparison t test. Asthma severity in atopic children was associated with fungal community composition (P = .001). By using logistic regression, asthma severity in nonatopic children was associated with total fungal concentration (odds ratio, 2.40; 95% CI, 1.06-5.44). The fungal genus Volutella was associated with increased asthma severity in atopic children (P = .0001, q = 0.04). The yeast genera Kondoa might be protective; Cryptococcus species might also affect asthma severity.
Conclusion
Asthma severity among this cohort of children was associated with microbial exposure, and associations differed based on atopic status.
All Author:
Karen C. Dannemiller Janneane F. Gent Brian P. Leaderer Jordan Peccia


——浙大迪迅 译
①儿童过敏性和非过敏性哮喘的严重程度可能受到微生物暴露的影响②我们试图研究家庭微生物暴露与儿童哮喘严重程度之间的关系。③参与者(n = 196)是从康涅狄格州和马萨诸塞州的一组哮喘儿童中挑选出来的。儿童按哮喘严重程度(轻度无症状或有最小症状需药物治疗或中度至重度持续性)和特应性状态(由血清IgE水平决定)进行分组。采用下一代DNA测序和定量PCR法测定室内粉尘中的微生物群落结构和浓度。利用Logistic回归研究哮喘严重程度与暴露指标之间的关系,包括丰度、微生物种类鉴定和量化、群落组成、总真菌和细菌浓度。④在所有儿童中,除了使用距离比较t检验的微生物群落组成外,还使用logistic回归分析,结果显示哮喘严重程度的增加与总变应原性真菌种类浓度的增加、真菌总浓度的增加和细菌丰度的增加显著相关。特应性儿童哮喘的严重程度与真菌群落组成有关(P = .001)。通过logistic回归分析,非变应性患儿哮喘的严重程度与总真菌浓度相关(优势比,2.40;95% CI, 1.06-5.44)。真菌属Volutella与特应性儿童的哮喘加重有关(P = 0.0001, q = 0.04)。酵母属Kondoa可能具有保护作用;隐球酵母也可能影响哮喘的严重程度。⑤在这一组儿童中,哮喘的严重程度与微生物暴露程度有关,并且根据周围环境的不同而有不同的关联。
延伸阅读
JACI
[IF:13.1]
Indoor microbial communities: Influence on asthma severity in atopic and nonatopic children
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.11.027
Abstract:
Background
Allergic and nonallergic asthma severity in children can be affected by microbial exposures.
Objective
We sought to examine associations between exposures to household microbes and childhood asthma severity stratified by atopic status.
Methods
Participants (n = 196) were selected from a cohort of asthmatic children in Connecticut and Massachusetts. Children were grouped according to asthma severity (mild with no or minimal symptoms and medication or moderate to severe persistent) and atopic status (determined by serum IgE levels). Microbial community structure and concentrations in house dust were determined by using next-generation DNA sequencing and quantitative PCR. Logistic regression was used to explore associations between asthma severity and exposure metrics, including richness, taxa identification and quantification, community composition, and concentration of total fungi and bacteria.
Results
Among all children, increased asthma severity was significantly associated with an increased concentration of summed allergenic fungal species, high total fungal concentrations, and high bacterial richness by using logistic regression in addition to microbial community composition by using the distance comparison t test. Asthma severity in atopic children was associated with fungal community composition (P = .001). By using logistic regression, asthma severity in nonatopic children was associated with total fungal concentration (odds ratio, 2.40; 95% CI, 1.06-5.44). The fungal genus Volutella was associated with increased asthma severity in atopic children (P = .0001, q = 0.04). The yeast genera Kondoa might be protective; Cryptococcus species might also affect asthma severity.
Conclusion
Asthma severity among this cohort of children was associated with microbial exposure, and associations differed based on atopic status.
All Author:
Karen C. Dannemiller Janneane F. Gent Brian P. Leaderer Jordan Peccia
2019-5-2 Artical
创建过敏性疾病的科研、科普知识交流平台,为过敏患者提供专业诊断、治疗、预防的共享平台。

MK手机投注 | 安博·体育(中国)有限公司-官网 | 乐动官方网站 | 星空手机版 | 星空手机版 | mk体育(MKsports集团)股份公司 | 安博手机网页版登录入口 | 华体平台 | 千亿体育官网在线登录入口中国有限公司 |
 华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
华亿体育(中国)游戏平台

